Hall Sensor Encoder
Hall Sensor Encoder
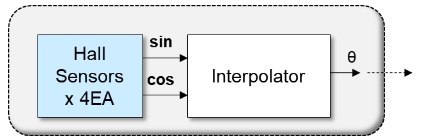
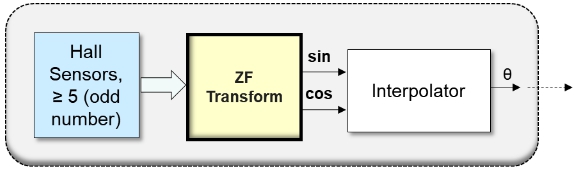
Hall sensor encoders are increasingly and widely used in industrial motor control systems due to its structural simplicity and durability in harsh environment at much less cost than resolvers or optical encoders. However, many external impairments as well as magnetic saturation introduce distortions in the sensing signals, and result in degraded accuracy of position detection. Typical Hall sensor encoders employ even number of Hall sensors, and from which two-phase orthogonal signals are sensed. ZF Hall sensor encoders employ odd N number of Hall sensors, and from which N-phase displacement signals are sensed. The sensed N-phase signals are ZF transformed to synthesize the two-phase orthogonal signals.
Typical Hall Sensor Encoders
- Sine and Cosine Signals are Sensed from the Even Number of Hall Sensors
ZF Hall Sensor Encoders
- N-phase Displacement Signals are Sensed from odd N Number of Hall Sensors
- Sine and Cosine Signals are Synthesized by the ZF Transform
ZF Transform Removes Harmonic Components by Non-linear Distortions
- Magnetic Saturation
- External Interferences
- Unbalanced and Asymmetric Structure
- Common Mode Noise
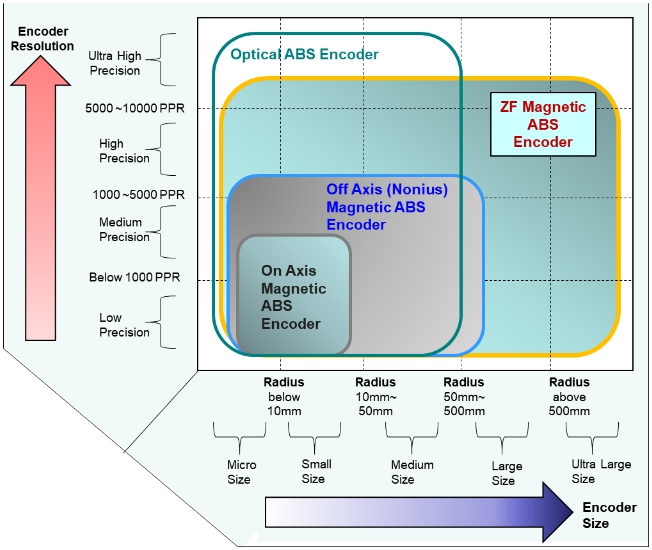
Resolution Comparison of Absolute Encoders
- Various Magnetic Encoders and Optical Encoders